A perfect connection: The combination of GIS and BIM significantly improves the data basis for important decisions in the urban planning context in construction projects.
Architectural planning is a complex process that requires a great deal of contextual information. To enable important urban planning decisions to be made at an early stage in order to deliver building plans that are ready for approval later on, planners use geographic information systems (GIS) and BIM (Building Information Modeling). By combining GIS and BIM data, urban context models can be generated, which - in addition to the usual 2D cadastral data and development plans - play an increasingly important role in architectural planning.
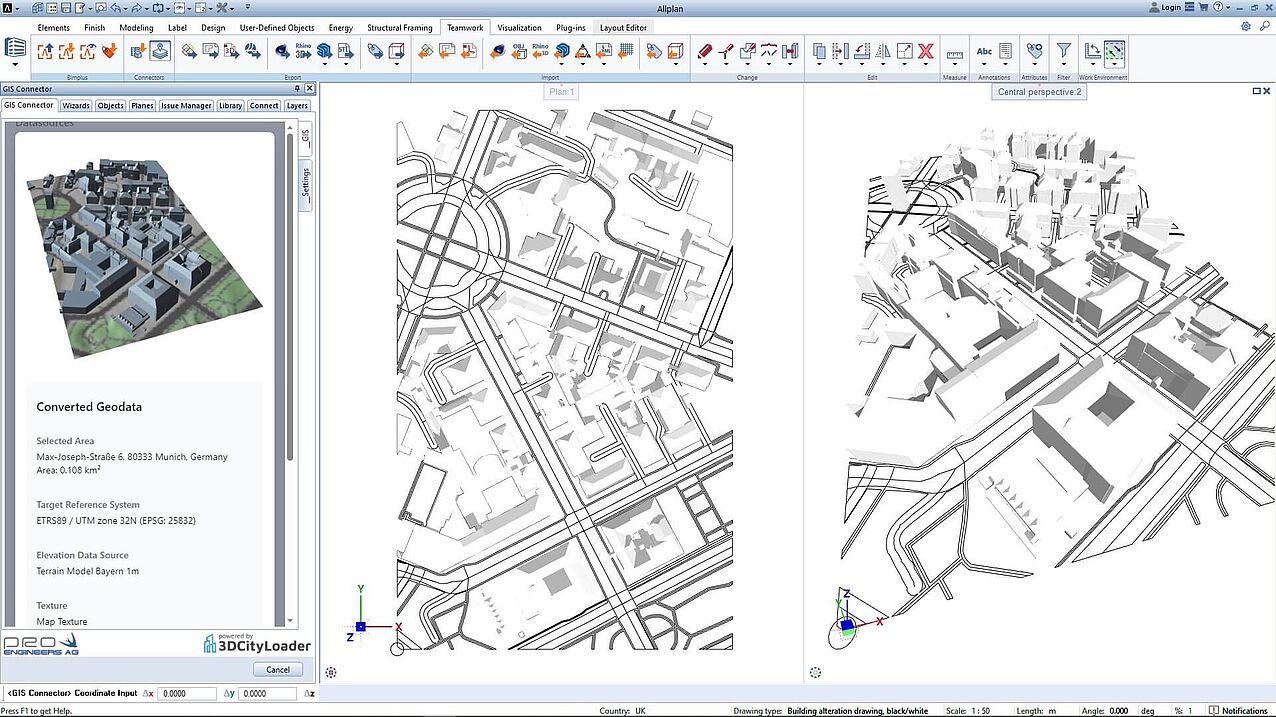
GIS in architectural planning
Geographic Information Systems are software tools that analyze, display and manage data on a large scale. In architectural planning, GIS are used to collect and analyze extensive geographic information about the urban context of the building site in question. This includes topographical data such as terrain models, infrastructural information (for example, on connections to the supply and disposal infrastructure or on traffic connections) as well as environmental data that define the perimeter of the construction project and have a significant influence on it. By integrating this data into the planning process, architects can gain a better understanding of the spatial environment and make informed decisions.
Context models through GIS and BIM
The combination of GIS and BIM enables direct model-based planning in context models. This enables a comprehensive representation of the planned building project in its urban context right from the start. By integrating GIS data into the BIM model, architects can not only view the building as such, but also understand its impact on the surroundings.
For example, factors such as solar radiation, wind patterns and urban infrastructure can be simulated in the BIM model to optimize the sustainability and functionality of the building. The topography model provides important insights into the height structure of the building site. The building cubature of the adjacent development provides the decisive information for the urban spatial quality of the intervention. In addition, it improves communication and cooperation between the planners and other project participants such as the building owner, the neighbors and the approval authorities.
GIS OpenData
GIS Open Data is geographic data that is freely accessible and usable by everyone. This data is provided by various organizations, authorities and institutions to facilitate access to geographic information. One such organization is Swisstopo - the Federal Office of Topography of Switzerland. Swisstopo offers a wide range of geographic data, including topographic maps, elevation data, aerial photographs and more. This data is available to the public free of charge and can be used by architects and other professionals to create accurate and detailed context models for architectural planning.
Internationally, more and more regions are making geodata available as open data. South Tyrol, the Netherlands and New York City already offer free access to digital city models. In Germany, Cologne, Hamburg, Berlin, North Rhine-Westphalia, Aachen, Lower Saxony, Hesse, Bavaria and Saxony are leading the way. Together with the GIS experts from 3D Cityloader, ALLPLAN is creating highly efficient workflows with the new Version 2024 to integrate this GIS data seamlessly into the planning process of architects. Learn more about GIS integration in ALLPLAN 2024 now.
Isn't it time you experienced the future of building design? Explore what ALLPLAN 2024 has to offer and take your projects to the next level with a free, 14-day trial.